Research
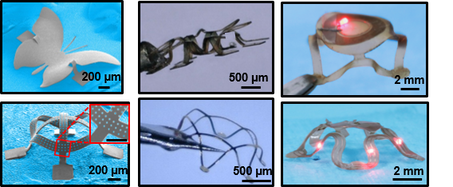 Freestanding 3D stretchable and shape-programmable architectures and electronics based on shape memory polymers
Freestanding 3D stretchable and shape-programmable architectures and electronics based on shape memory polymers
Design and manufacturing of stretchable 3D architectures and electronics
Complex three-dimensional (3D) functional architectures are of widespread interest due to their potential applications in biomedical devices, metamaterials, energy storage and conversion platforms and electronics systems. Our goal is to explore mechanics-guided assembly approach and its combination with existing technologies such as 3D printing for 3D architectures and electronics. Materials of interest include smart materials (shape-programmable materials), metals and a heterogeneous combination of those materials. We will also explore the various applications of 3D architectures and electronics.
Complex three-dimensional (3D) functional architectures are of widespread interest due to their potential applications in biomedical devices, metamaterials, energy storage and conversion platforms and electronics systems. Our goal is to explore mechanics-guided assembly approach and its combination with existing technologies such as 3D printing for 3D architectures and electronics. Materials of interest include smart materials (shape-programmable materials), metals and a heterogeneous combination of those materials. We will also explore the various applications of 3D architectures and electronics.
Soft materials and systems
Soft materials, which can be easily deformed when exposed to external stimuli, have attracted considerable attention in various applications such as stretchable and biointegrated electronics, advanced energy harvesting and storage, soft robotics and machines, sensory skins, and drug delivery. Our goal is to design and fabricate soft materials and systems that can be used for various applications. In particular, we are working on liquid crystal elastomers, including the molecular-material-structure correlations, local programming, and stiffness heterogeneity, as well their applications in soft robotics and others.
Soft materials, which can be easily deformed when exposed to external stimuli, have attracted considerable attention in various applications such as stretchable and biointegrated electronics, advanced energy harvesting and storage, soft robotics and machines, sensory skins, and drug delivery. Our goal is to design and fabricate soft materials and systems that can be used for various applications. In particular, we are working on liquid crystal elastomers, including the molecular-material-structure correlations, local programming, and stiffness heterogeneity, as well their applications in soft robotics and others.
Soft, pressure-tolerant electronics
We have been developing soft, pressure-tolerant electronics for applications in harsh environments including the large hydrostatic, salinity ocean, and testing the electronics in the lab (pressure vessel) and field settings.
We have been developing soft, pressure-tolerant electronics for applications in harsh environments including the large hydrostatic, salinity ocean, and testing the electronics in the lab (pressure vessel) and field settings.